Investing is one of the most effective ways to preserve and grow capital over the long term. Experts at Trading Academy emphasize that successful investing requires a systematic approach, patience, and ongoing learning. Modern investment opportunities include traditional financial instruments like stocks and bonds, cryptocurrencies, real estate, and digital assets. The Pocket Option platform offers access to derivatives for active trading. In this article, we’ll cover the basics of investing, asset types, minimum starting amounts, and a step-by-step action plan for beginning investors.
Investing is one of the most effective ways to preserve and grow capital over the long term. Experts at Trading Academy emphasize that successful investing requires a systematic approach, patience, and ongoing learning. Modern investment opportunities include traditional financial instruments like stocks and bonds, cryptocurrencies, real estate, and digital assets. The Pocket Option platform offers access to derivatives for active trading. In this article, we’ll cover the basics of investing, asset types, minimum starting amounts, and a step-by-step action plan for beginning investors.
What is investing in simple terms for a beginner
Investing is putting money into assets with the goal of generating income or future value appreciation. Instead of letting your money sit in a regular account and lose value due to inflation, you’re buying something that can grow in value or generate regular income.
A simple analogy:
Imagine you bought an apple orchard for $10,000. A year later, the trees produced fruit, which you sold for $1,000 (10% profit). Five years later, the orchard has grown, and it’s now worth $15,000. You’ve received both regular income (the harvest) and capital gains (the increase in the value of the orchard). That’s how investing works.
Key differences between investing and speculation:
Investments:
- Long-term perspective (from one year or more).
- Focus on the fundamental value of the asset.
- Willingness to survive temporary setbacks.
- Diversification to reduce risks.
- Passive or moderately active approach.
Speculation (trading):
- Short-term trades (from minutes to weeks).
- Betting on price fluctuations, not value.
- Active management and continuous monitoring.
- High risks and potential returns.
- Deep expertise and time are required.
Most beginners confuse investing with trading and lose money trying to get rich quick. Real investing is a marathon, not a sprint.
Basic requirements for investors
Successful investing requires more than just money; it also requires the right mindset, knowledge, and discipline.
Financial safety cushion:
Before you begin investing, create a reserve of 3-6 months’ worth of expenses in a regular bank account or savings account. This will protect you from having to sell your investments at a loss in the event of unexpected expenses (job loss, renovations, medical treatment).
Basic knowledge:
- Understanding the main types of assets and their risks.
- Knowledge of the principles of diversification.
- Basic financial literacy (what is profitability, volatility, liquidity).
- Ability to read financial information and news.
You don’t have to be an expert, but a basic understanding is crucial. Investing in unknown instruments is a recipe for losses.
Psychological stability:
- Be prepared for temporary losses without panicking.
- Discipline – do not sell assets at the first drawdown.
- Long-term thinking – focus on years, not days.
- Control of emotions (greed and fear).
Most investor mistakes are psychological, not technical.
Time horizon:
Investments take time to grow. The minimum horizon for risky assets (stocks, crypto) is 3-5 years. If you need money sooner, invest in more conservative instruments or not invest at all.
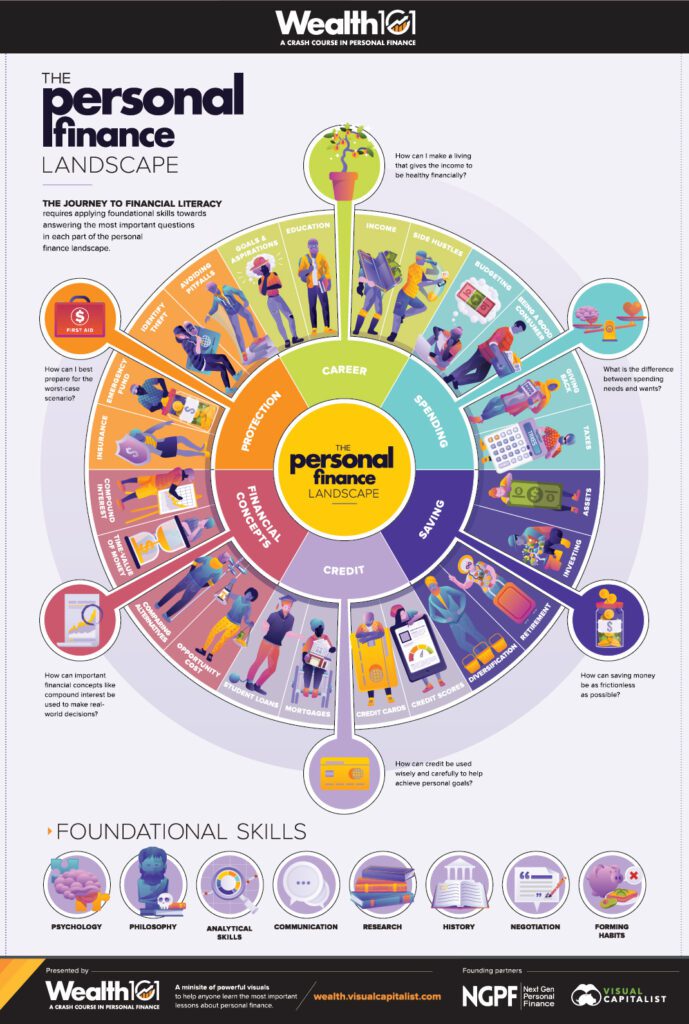
Personal Finance Landscape: Basic Skills
Why Personal Investing?
Inflation protection:
Money in a regular account loses purchasing power. With inflation at 5-10% per year, in 10 years, $10,000 will be worth $5,000-6,000 today. Investing in assets that grow faster than inflation preserves and grows capital.
Creating Passive Income:
Stock dividends, bond coupons, and rental income from real estate are all sources of passive income that work for you without your active participation.
Achieving financial goals:
- Pension is savings for old age.
- Children’s education – tuition fees.
- Large purchases – a house, a car.
- Financial independence – living on investment income.
Without investing, achieving these goals through salary alone is extremely difficult.
Money working for you:
Active income (salary) is limited by your time. Investment income grows exponentially thanks to compound interest—profits are reinvested and begin to generate profits of their own.
Example: $10,000 at 10% per annum becomes $67,000 after 20 years thanks to reinvestment. Without compounding, it would only be $30,000.
What types of investments are there?
Let’s describe the main types.
Акции
Buying shares in companies. Earn on share price growth and dividends. High potential returns (historically 10-15% per annum), but also high volatility.
Suitable for: long-term investors with a 5-year horizon.
Bonds
Debt securities—you lend money to a government or company at a fixed interest rate. The yield is lower (5-8%), but they’re more stable and safer than stocks.
Suitable for: conservative investors and portfolio diversification.
Real Estate
Purchase of residential or commercial property for rent or resale. Stable rental income (5-8% per annum of the property value) and growth in value, but requires significant capital and management.
Suitable for: investors with capital of $50,000 and a willingness to manage the asset.
Cryptocurrencies
Digital assets on the blockchain (Bitcoin, Ethereum, altcoins). Extreme volatility – you can gain 100%+ or lose 50% in a year. A high-risk asset for diversification.
Suitable for: investors prepared to accept high risks and the potential loss of their entire crypto investment.
ETFs and index funds
A basket of assets (stocks, bonds) that you own through a single instrument. Automatic diversification, low fees, simplicity. They track the market index.
Suitable for: Beginner investors looking for simple diversification.
Precious metals
Gold, silver, platinum. They offer protection against inflation and crises, but they don’t generate income (no dividends or coupons). A conservative asset for diversification.
Suitable for: the protective part of the briefcase (5-10%).
Digital assets (websites, domains, NFTs)
Owning websites that generate advertising revenue, domains for resale, and NFTs. Requires digital expertise.
Suitable for: investors with an understanding of internet business.
P2P lending
Issuing loans to individuals or businesses through platforms. Profitability is 10-20%, but there is a risk of borrower default.
Suitable for: portfolio diversification with small amounts.
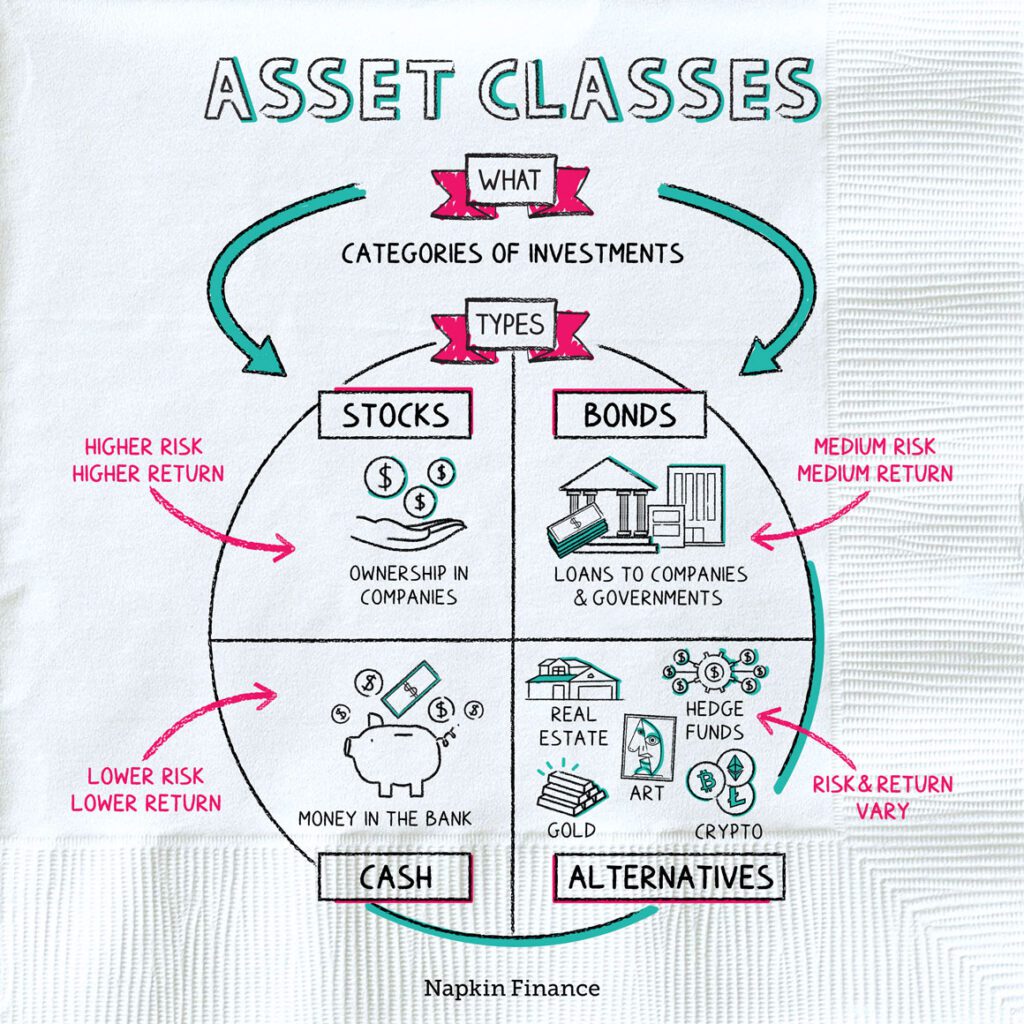
Asset classes: stocks, bonds, cash
Minimum investment amount
A common myth: “You need tens of thousands of dollars to get started.” Reality: You can start with much less.
Minimum amounts by asset type:
Stocks through a broker: from $50-100. Many brokers allow you to buy fractional shares—you can buy 0.1 Apple share for $20-30.
Bonds: from $50-100. Depends on the par value of specific issues.
ETF: from $50-100. One ETF provides diversification across hundreds of companies.
Cryptocurrencies: from $10-20. You can buy fractions of a Bitcoin or altcoins with minimal amounts.
P2P lending: from $10-50. Platforms allow you to diversify small amounts across multiple loans.
Real Estate: Starting at $50,000 for outright purchase. Alternatives include REITs (real estate investment trusts) starting at $100.
Recommended amounts for a meaningful start:
- Minimum: $500-1,000 – you can create a diversified portfolio of ETFs and several stocks.
- Comfortable: $3,000-5,000 — full diversification across asset classes and instruments.
- Optimal: $10,000+ – ample opportunities for strategy and diversification.
The key isn’t the initial capital size, but the regularity of deposits. Investing $100-200 monthly yields better results than a one-time investment of $5,000 with no further deposits.
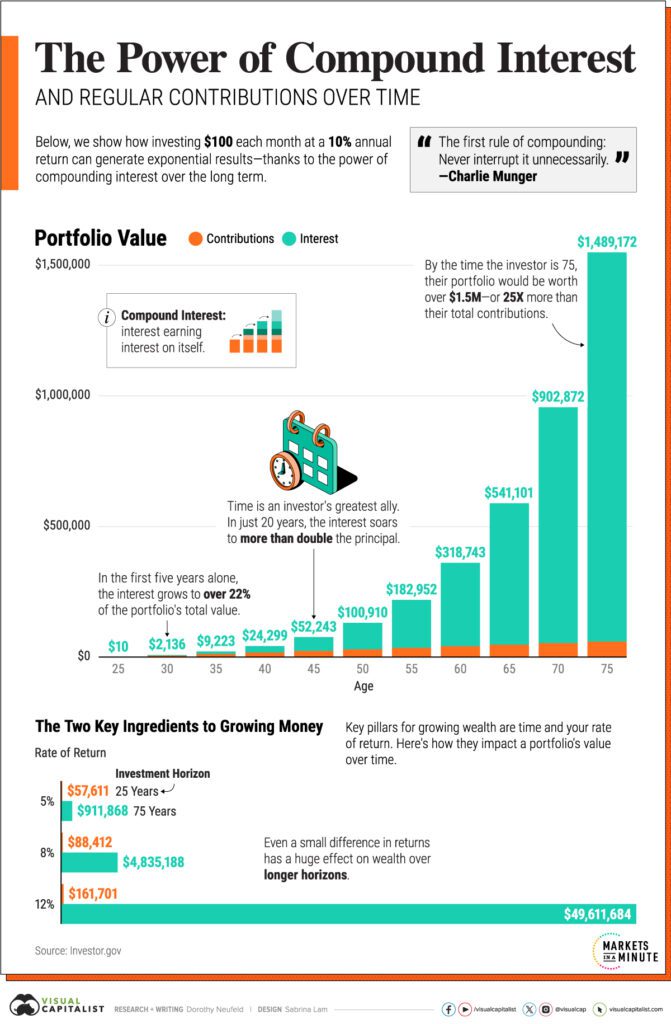
Compound interest: $100 monthly contributions
Where a beginner should invest
Asset selection principles for beginners:
Diversification is the cornerstone:Don’t put all your money into one asset or even one asset class. The classic structure for beginners:
- 60% — conservative assets (bonds, index ETFs).
- 30% — shares of large, stable companies (blue chips).
- 10% — high-risk assets (crypto, startups, altcoins).
Start with liquid instruments that are easy to sell at market price (stocks, ETFs, crypto on major exchanges). Avoid illiquid investments like startups or exotic assets.
Understandability:Invest only in what you understand. If you can’t explain how an asset works and where its income comes from, don’t invest.
Specific tools for beginners:
ETF on broad indices:- S&P 500 ETF — the top 500 US companies.
- World ETF – diversification across the globe.
- Bond ETF – a basket of bonds for stability.
Advantages: automatic diversification, low fees, simplicity.
Blue chips (large companies):- Technology giants (Apple, Microsoft, Google).
- Financial sector (JPMorgan, Visa).
- Consumer goods (Coca-Cola, Procter & Gamble).
Stable companies with a long history and dividends.
Bitcoin and Ethereum:If you’re prepared to take on high risks, allocate 5-10% of your portfolio to top cryptocurrencies. Avoid lesser-known altcoins and memecoins.
Avoid at the start:- Complex derivatives (options, futures) – for experienced traders.
- Little-known startups – high risk of total loss.
- Exotic assets (wine, art) require expertise.
- Forex with high leverage is a path to quick losses.
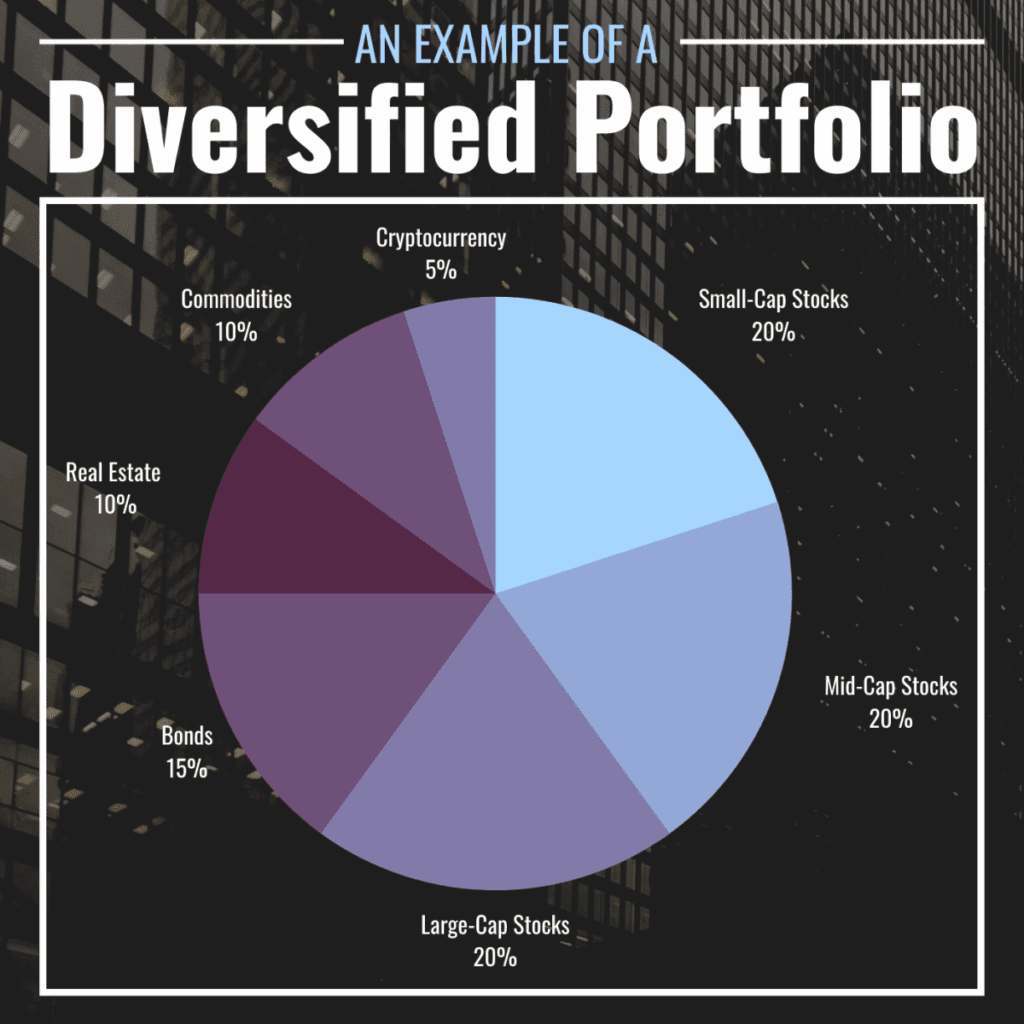
Example portfolio: stocks/bonds/cash/real
Pocket Option as an Investment Platform
The Pocket Option platform provides access to derivatives trading with fixed profit and loss potential.
Platform Features:
- Simplified interface, aimed at beginners.
- Short contracts from 60 seconds to several hours.
- Demo account for practice without real investment.
- Low entry threshold—you can start with minimal deposits.
Important restrictions:
This is not long-term investing, but active trading. Derivatives require constant involvement, technical knowledge, and a high level of psychological stability. It is a speculative activity with a high risk of capital loss.
Regulatory Restrictions: In countries of the European Economic Area (including Germany), binary options trading for retail investors is prohibited by permanent measures of the ESMA. A similar ban is in effect in the UK under the FCA. Services are not available to residents of the EEA, UK, US, and several other jurisdictions. Be sure to check the legality in your country.
Statistics: According to regulators, most retail accounts lose money on derivatives. This is only suitable for experienced traders who understand all the risks, and not for classic long-term investing.
Methods of trading on exchanges
Spot trading:
Buying assets with immediate delivery. Buy a stock or cryptocurrency—it’s yours to hold as long as you like. This is classic investing.
Advantages:
- Physical possession of an asset.
- There is no expiration date for this position.
- No risk of liquidation.
- Easy for beginners.
Disadvantages:
- Earnings only on growth (for long positions).
- Full amount required for purchase.
- Slower capital growth compared to leverage.
Margin Trading:
Trading with borrowed funds from a broker. Leverage allows you to control a position larger than your capital, but it also increases both profits and losses.
Advantages:
- Increased profit potential.
- Possibility of short positions (earning on the fall).
Disadvantages:
- Liquidation risks when moving against a position.
- Interest for using borrowed funds.
- High psychological stress.
Not recommended for beginners without experience and understanding of the risks.
Futures and Derivatives:
Contracts to buy/sell an asset in the future. Traded on crypto exchanges and traditional platforms. Built-in leverage, high risk.
Only for experienced traders with a deep understanding of the mechanics.
Recommendation for beginners:
Start with spot trading. Buy assets without leverage, hold them long-term, and reinvest dividends. Margin trading and derivatives are only possible after a year or more of experience and extensive training.
Step-by-step instructions for trading on the Bybit exchange
Bybit is a popular cryptocurrency exchange with an intuitive interface and a wide selection of tools for investing in crypto.
Step 1. RegistrationGo to the official Bybit website and register using email or phone number. Create a strong password and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for security.
Step 2. Verification (KYC)Please complete identity verification by uploading documents (passport, driver’s license). This is required for full access to the exchange’s functionality and withdrawals.
Step 3. Account replenishmentDeposit funds using a bank card, P2P (purchasing from other users), or by transferring cryptocurrency from another exchange. Beginners may find it easier to use a card to purchase USDT (stablecoin).
Step 4. Selecting an asset for investmentFor long-term investment:
- Click “Spot” (spot trading) in the top menu.
- Select a trading pair, such as BTC/USDT (Bitcoin to Dollar).
- Learn the chart and basic information about the coin.
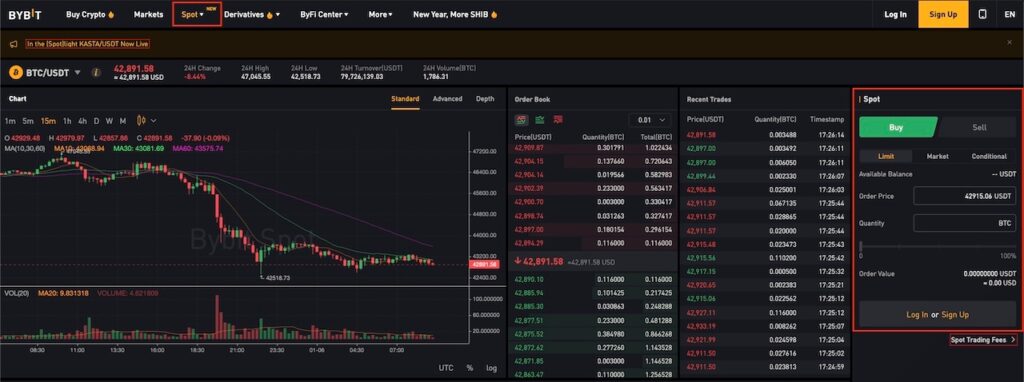
Bybit Spot: BTC chart and book
Step 5. Buying Cryptocurrency- In the right panel, select the order type:
- Market — purchase at the current market price (instantly).
- Limit – buy at the price you specify (when the market reaches the level).
- Enter the amount in USDT or the number of BTC.
- Confirm your purchase by clicking the “Buy BTC” button.
For investors, we recommend a Market order—it’s simple and fast.
Step 6. Storage of assetsAfter purchasing, the cryptocurrency is stored in your Spot wallet on the exchange. For long-term storage of larger amounts, consider transferring it to a cold wallet (hardware wallet) for maximum security.
Step 7. DCA Strategy (Averaging)Don’t buy the entire amount at once. Divide your capital into parts and buy regularly (for example, once a week or month). This reduces the risk of entering at a price peak.
Step 8. Monitoring and RebalancingCheck your portfolio monthly. Don’t sell at every dip—hold for the long term. Rebalance quarterly if your asset mix has changed significantly.
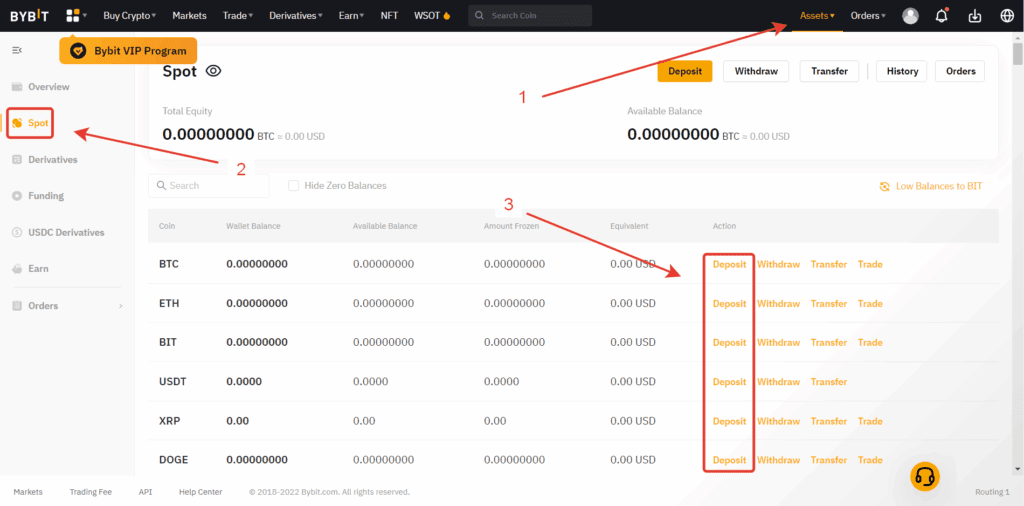
Assets page: list of coins on the right
What mistakes do beginning investors most often make?
Lack of strategy and plan:
Mistake: Buying whatever comes to mind based on emotions or online advice. Correct: Define your goals, investment horizon, and risk profile. Create an asset allocation plan.
Panic selling during drawdowns:
Mistake: Selling assets when prices fall 10-20% out of fear of further losses. Correct: Realize that volatility is normal. The S&P 500 has fallen 30-50% several times, but it always recovered and rose further.
The pursuit of quick profits:
Mistake: Investing in “hot” assets (memcoins, hyped stocks) in hopes of getting rich quick. Correct: Focus on fundamentally strong assets with long-term potential. Quick profits = high risk.
Lack of diversification:
Mistake: Putting all your money into one stock or cryptocurrency. Correct: Spread your capital across 10-20 assets across different sectors and classes.
Ignoring fees and taxes:
Mistake: Not considering that frequent trades eat into profits with commissions, and taxes reduce the final income. Correct: Minimize the number of trades (buy and hold), taking into account the tax implications.
Investing with borrowed funds:
Mistake: Taking out a loan or using your last money for investments. Correct: Investing only available funds that you’re willing to lose.
Ignoring Learning:
Mistake: Investing in unfamiliar instruments without learning the basics. Correct: Constantly learn, read books, follow financial news, and analyze your mistakes.
FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out):
Mistake: Buying an asset after a strong rally, fearing missing out on profits. Correct: Buy during corrections and according to a plan, not based on emotion. If something has grown tenfold, you’re probably too late.
Checking portfolio too often:
Mistake: Looking at prices every day and reacting to short-term movements. Correct: Checking monthly or quarterly. Frequent monitoring increases anxiety and leads to impulsive decisions.
Critical Risk Alerts
Investments do not guarantee profit and always involve the risk of capital loss. All financial markets are volatile—asset prices can fall by 30-50% even in the short term.
Past performance does not guarantee future returns. Just because an asset has grown for 10 years doesn’t mean it will continue to grow. Markets are cyclical—periods of growth alternate with crises.
Diversification reduces, but does not eliminate, risk. Even a well-diversified portfolio can lose 20-40% during a crisis. Be prepared for drawdowns and avoid investing money you’ll need in the next 3-5 years.
Invest only available funds. Never loans, last savings, money for housing, education, or medical treatment. This article is for educational purposes only and is not financial advice. You make all decisions at your own risk.
Conclusion
Investing is a powerful tool for building long-term wealth, but it requires patience, discipline, and ongoing learning. Start small, focus on diversification and the long term, and avoid emotional decisions. The first few years may be challenging, but a systematic approach will pay off over time.The Pocket Option platform offers tools for active trading, but this is more of a speculative activity than traditional investing. To gain fundamental knowledge of financial markets, investment strategies, and capital management, study the educational programs at the Trading Academy, which presents up-to-date methods for working with various assets and building an investment portfolio.